Eye diseases
Blocked tear duct
What is a blocked tear duct?
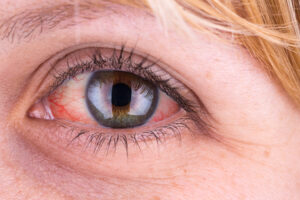
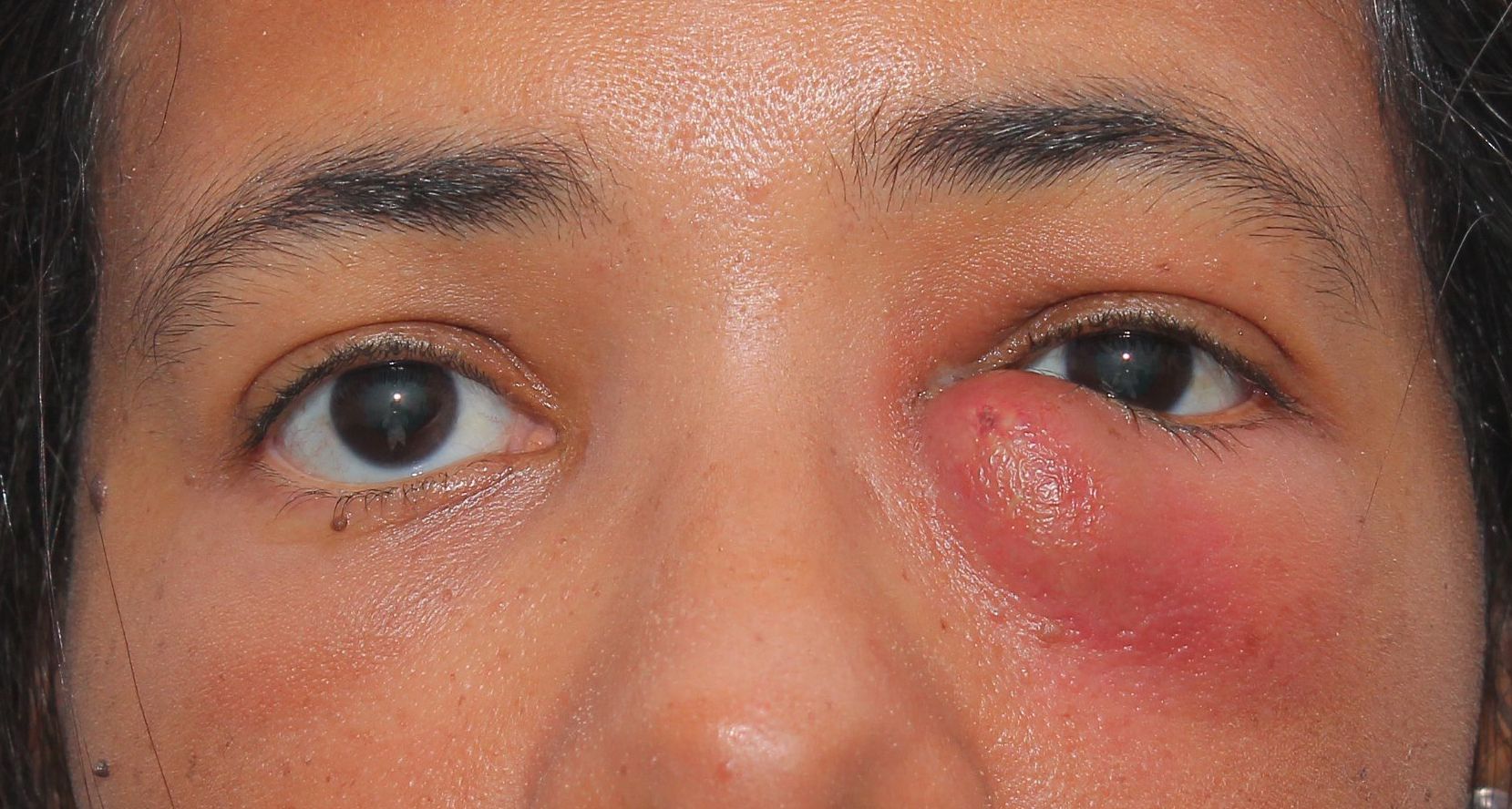
A blocked tear duct is an eye disorder that occurs when the duct through which tears normally drain (which runs from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity) becomes fully or partially blocked for different reasons. This means that the tears are unable to drain properly and are accumulated on the eye’s surface.
This is generally not a serious disorder, but it is extremely bothersome and can irritate the eye, as well as increasing the risk of inflammatory processes and recurrent infection, due to the spread of bacteria in the blocked duct. You must in all cases consult an ophthalmologist, because tumours located in areas near the nose can cause blocked tear ducts and be a severe cause behind this problem.
Symptoms
Causes and risk factors
Treatment
Tears are produced in the lacrimal gland below the eyebrow, from where they are carried to the eye to bathe and lubricate it. They then reach the nose through the lacrimal points that are on the inner edge of the eye. When tear ducts become blocked, this leads to excessive, constant tearing, with tears flowing because their “drainage” is not working.
This watery eye is sometimes accompanied by conjunctivitis. Blocked tear ducts can also lead to painful inflammation of the inner corner of the eye, and can encourage secretion (rheum) on the eyelids and on the surface of the eye, which can also cause blurred vision.