Treatments
Orbital decompression
What is orbital decompression?
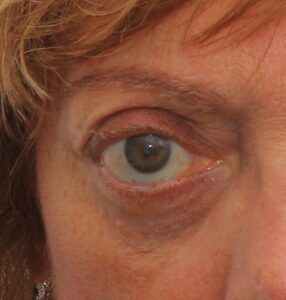
Orbital decompression is a surgical procedure we perform to enlarge the orbit that houses the eyeball and its attachments. Thanks to this surgery, we relieve the pressure on the orbital cavity that is exerted by tissues and eye structures that are enlarged for different reasons, which can compress the optic nerve and cause irreversible damage, if action is not taken early. Furthermore, by repositioning the eye and preventing it from protruding due to lack of space, it also appears less prominent, and we achieve a clear aesthetic improvement.
To widen the orbital cavity, our oculoplastic surgeons cut and remove segments of the bone that make up the walls of the orbit, while also removing fatty tissue. The incisions made to access the eye socket are tiny and usually highly concealed after the minimally invasive procedure.
Eye diseases treated by orbital decompression
One of the consequences of thyroid orbitopathy (inflammation of the orbit) is exophthalmos or “bulging eyes”. There are also other reasons for orbital decompression, such as eye tumours or cases of severe congenital glaucoma, a disease that can cause the eyes to be larger than usual.
Recovery
Orbital decompression is a fast recovery surgery, in which you have to follow the antibiotic and anti-inflammatory treatment we prescribe to avoid complications. We will also indicate relative rest for a few days, during which you should avoid professional or personal activities that involve the risk of suffering any trauma to the face.
The first days after the surgery you may notice a slight swelling and redness or bruising of the eyelids. Postoperative double vision is rare, although it is normal and gradually stabilises. After approximately one month, we will ask you to come for a check-up at the Miranza clinics to assess the final results and check that the postsurgical evolution has been correct.